Medicibal Benefits of Cinnamon



The Medicinal Benefits of Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a common spice that can be found in different types of bread, desserts, hot drinks, even alcohol. Even though cinnamon has been used for it’s medicinal properties since ancient Egypt, not too many people today know how to utilize this precious resource. This article will detail the top medicinal benefits of cinnamon.
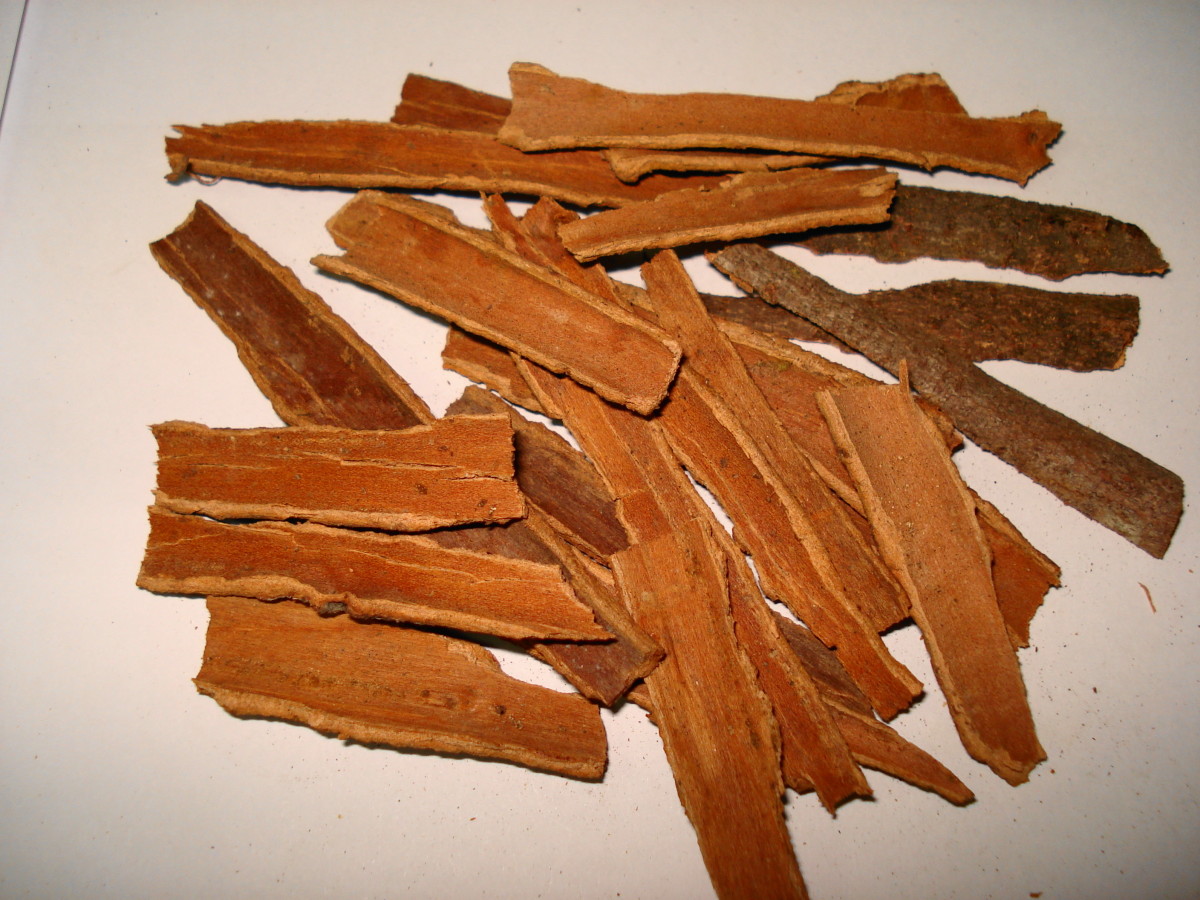
Cinnamon spice comes from that inner bark of the Cinnamomum tree. The active ingredient in cinnamon that contains the healthful ingredient is cinnamaldehyde (Cooper, 2005). There are two types of cinnamon in usage today, Ceylon cinnamon, and cassia cinnamon. Ceylon cinnamon is more commonly known as “true cinnamon”, and contains higher levels of cinnamaldehyde than cassia cinnamon, which is the most frequent cinnamon found in grocery stores (Miller & Chen, 2010).
Since the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved cinnamon for the treatment or prevention of any ailments, there is no set medical standard on the amount of cinnamon needed to reach a therapeutic level. However, medical experts who specialize in alternative medicine recommend a therapeutic level of at least one teaspoon of Ceylon cinnamon a day, but no more than six teaspoons per day (Cooper, 2005).
Cinnamon has been used for it’s medicinal benefits for thousands of years. Cinnamon was considered such a sacred resource, a natural antibiotic, that pharaohs were buried with it in case they might need it in the next life (Pratt & Matthews, 2006). Cinnamon has been historically used in conjunction with honey, not only for the pleasing taste but also because when the two ingredients are combined, it can help strengthen white blood cells (Cooper, 2005). When honey and cinnamon are consumed in a form of a drink (such as a tea), the two ingredients can help an individual recover from a cold faster, treat a cough or respiratory infection, even heal a bladder infection.
Another medicinal benefit of cinnamon is it’s ability to reduce chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is commonly the result of the body’s immune system being compromised, whether the result of an infection, poor diet, stress, lack of sleep, too much alcohol intake, and so forth. This inflammation can contribute to heart and lung disease, diabetes, even cancer (Pratt & Matthews, 2006). By consuming a therapeutic level of cinnamon each day, the body will begin to process cinnamaldehyde as a low-level blood thinner.
Lastly, cinnamon has been shown to help diabetic patients. A 2011 study conducted by the Mayo Clinic showed that patients with type 2 diabetes who took two 500 milligrams cinnamon pill per day for three months had a positive result on their glycemic index (Miller & Chen, 2010). Another study in 2004 showed that when patients who had severe difficulty controlling their type 2 diabetes utilized the common diabetic drug Metformin in conjunction with cinnamon supplements, the majority of these patients were then better able to control their insulin levels.
As with any new medical regimen, a person who wishes to use cinnamon for medical benefits should seek counsel from a doctor first. While it is rare that cinnamon would cause any negative side-effects, in some people, cinnamon can cause sores, redness, and irritation around the mouth (Pratt & Matthews, 2006). In large doses, cinnamon can be fatal, especially to those who suffer from ailments of the liver; this is one reason taking part in the “cinnamon challenge” can prove fatal. For individuals who can utilize cinnamon therapeutically, the medical benefits of this common spice are significant.
References
Cooper, C. (2005). Handbook of Stress Medicine and Health (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press.
Miller, G. & Chen, E. (2010). Stress, Immunity, and Disease. Handbook of Stress Medicine and Health, Second Edition, 131-154.
Pratt, S., & Matthews, K. (2006). Superfoods Healthstyle: Proven Strategies for Lifelong Health. New York: William Morrow.